

Under the MBR partitioning scheme, there are three different types of partitions – Primary, Extended, and Logical. Those storage units are called partitions.
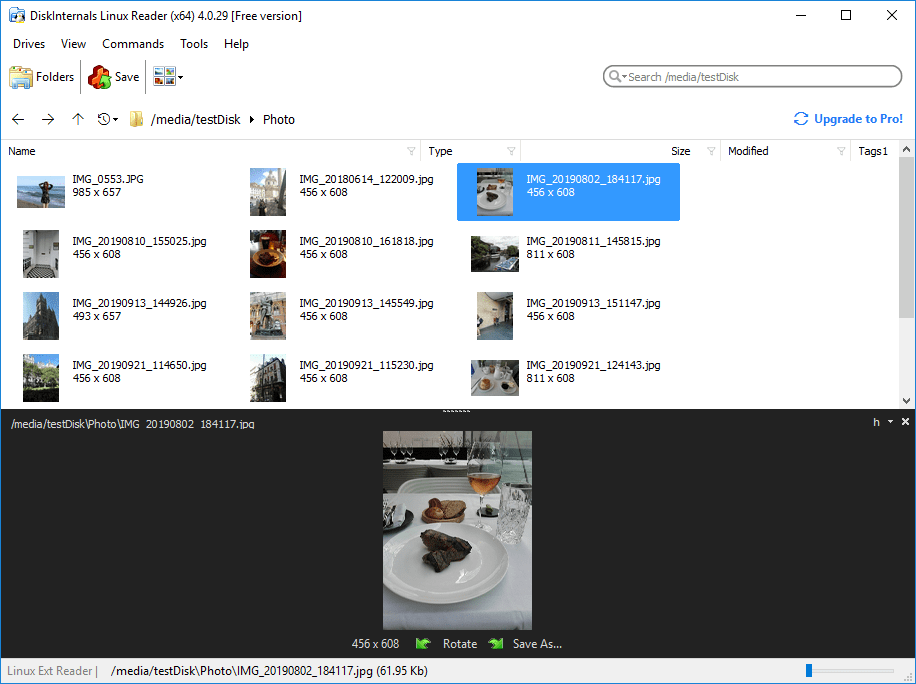
#Linux drive reader install
Partitions and Partition Numbering: To install an operating system on a hard drive, it must first be subdivided into distinct storage units.
You should see two options – EFI Compatible ROM and Legacy ROM. Under the Boot menu, look for PCI ROM Priority. You can also tell whether GPT or MBR is in use by accessing the UEFI setup utility. The Disklabel type: gpt line confirms that GPT is in use.įigure 5: This output of fdisk -l shows MBR in use
#Linux drive reader windows
If you’re already running a Linux distribution or attempting to install one on a recent Windows 7/8 computer, the easiest method of finding out what partitioning standard is used is to launch a shell terminal and type sudo fdisk -l (leave out the sudo if the distribution does not use it).įigure 4 shows the output of sudo fdisk -l from a Ubuntu Linux installation.
#Linux drive reader windows 8
If you bought a Windows 8 computer, it’s most certainly installed on a GPT partitioning scheme. Newer computers come with a replacement firmware for the old BIOS system called UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware interface), and GPT is a part of the UEFI standard. Those partitions are called primary partitions.

Most of the highly technical terms associated with this subject have been omitted, so this should be an easy read.

An understanding of all the aspects concerning how a disk is referenced and partitioned will put you in a better position to troubleshoot installation and disk-related problems. You’ll read about hard drive naming convention in Linux, how they are partitioned, partition tables, file systems and mount points.īy the time you are through reading this, you should have a pretty good idea of what you are doing when installing your next Linux distribution on your laptop or desktop computer. If you are migrating from Windows to Linux and are attempting to install any Linux distribution alongside Windows 7/8 on your computer, this article should come in handy. It is intended to be an absolute beginner’s guide to understanding how Linux handles disks and partitions. You can read the updated post at What you need to know about disks and disk partitions in Linux.Ī beginner’s guide to disks and disk partitions in Linux is an updated version of Guide to disks and disk partitions in Linux. Author’s Note: This post has been updated with added info about NVMe SSDs, or PCIe SSD disks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
